World Water Day is observed annually on March 22nd to raise awareness about the importance of freshwater and advocate for the sustainable management of water resources. It’s a day to highlight and discuss the significance of water and water-related issues such as access to clean water, sanitation, water scarcity, and conservation efforts.
Origin of World Water Day
World Water Day originated from the 1992 United Nations Conference on Environment and Development in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. During this conference, the United Nations General Assembly adopted Resolution A/RES/47/193, which declared March 22nd as World Day for Water. The first World Water Day was observed the following year, in 1993.
What is done on World Water Day
It’s a day to highlight water-related issues such as access to clean water, sanitation, water scarcity, and conservation efforts.
Access to clean water : Access to clean water refers to the ability of individuals and communities to obtain water that is safe for drinking, cooking, personal hygiene, and other domestic uses. Clean water is free from harmful contaminants, such as bacteria, viruses, chemicals, and pollutants, that can cause waterborne diseases and health problems.
Access to clean water is a fundamental human right, essential for ensuring public health, sanitation, and overall well-being. It is also crucial for supporting various aspects of daily life, including agriculture, industry, and economic development.
Water Sanitation : Water sanitation refers to the provision of facilities and services that ensure safe and hygienic conditions for water use, particularly for drinking, cooking, personal hygiene, and other domestic purposes. It involves treating and managing water to remove contaminants and harmful microorganisms that can cause waterborne diseases and health problems.
Water Scarcity : Water scarcity refers to a situation where the demand for water exceeds the available supply of freshwater resources within a particular region or community. It occurs when there is insufficient water to meet the needs of various users, including households, industries, agriculture, and ecosystems.
Conservation efforts : Water conservation efforts involve actions and strategies aimed at reducing water consumption, minimizing waste, and preserving freshwater resources for future generations. These efforts are crucial for addressing water scarcity, promoting sustainability, and ensuring access to clean water for all. Some key water conservation efforts include:
How to conserve Water
1. Efficient Water Use: Encouraging individuals, households, businesses, and industries to use water more efficiently by adopting water-saving practices and technologies. First of all self awareness is crucial in this aspect. Without knowing the importance of water and its need to conserve the same, it is difficult to bring the efficiency in the usage of water.
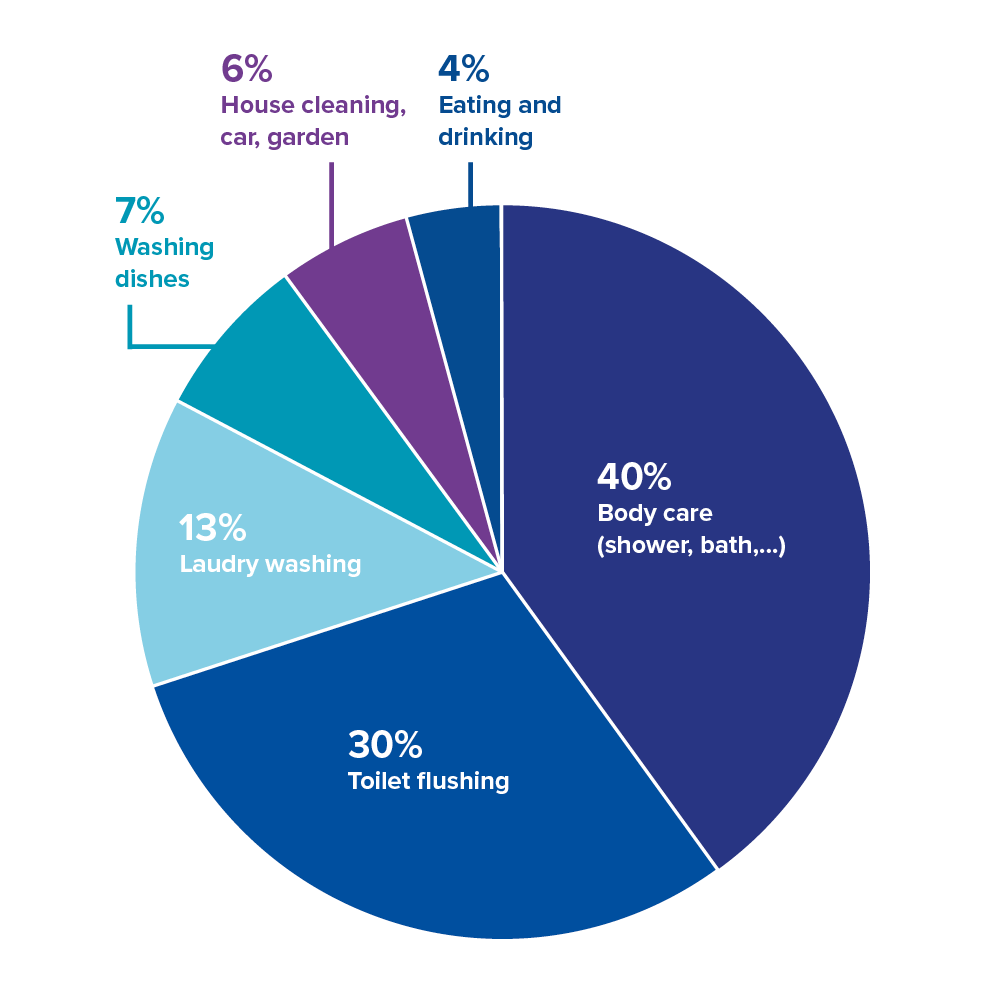
Water conservation technologies may include installing low-flow fixtures, such as faucets, showerheads, and toilets, using water-efficient appliances, implementing irrigation systems with smart controllers, and fixing leaks promptly.
2. Water-Efficient Landscaping: Promoting water-efficient landscaping practices, such as xeriscaping, which involves designing landscapes with drought-tolerant plants, mulch, and efficient irrigation techniques to minimize water use in outdoor spaces.
3. Agricultural Water Management: Implementing water-saving irrigation techniques and practices in agriculture, such as drip irrigation, precision farming, and soil moisture monitoring, to optimize water use efficiency and minimize water waste in crop production.
4. Rainwater Harvesting: Capturing and storing rainwater for later use in landscaping, irrigation, and non-potable applications through rainwater harvesting systems, such as rain barrels, cisterns, and rooftop collection systems. There are many cases globally where drought prone areas turned into green beds post rain water harvesting and construction of check dams.
5. Greywater Recycling: Recycling and reusing greywater (wastewater from sinks, showers, and laundry) for non-potable purposes, such as landscape irrigation, toilet flushing, and industrial processes, to reduce freshwater demand and wastewater generation.
6. Policy and Regulation: Enacting and enforcing water conservation policies, regulations, and incentives at the local, regional, and national levels to promote efficient water use, discourage water waste, and protect water resources. This may include water pricing mechanisms, water efficiency standards, building codes, and water conservation rebates or incentives. The governments globally adopt water conservation acts and policies.
7. Public Awareness and Outreach: Raising awareness about the importance of water conservation and providing education and outreach programs to inform individuals, communities, and businesses about water-saving practices, behavior changes, and the benefits of water conservation.
8. Community Engagement: Engaging communities, stakeholders, and local organizations in water conservation initiatives through partnerships, collaboration, and participatory approaches to foster a culture of water stewardship and collective action.
By implementing these water conservation efforts, communities can reduce water consumption, minimize water waste, and preserve freshwater resources for current and future generations, while also promoting sustainability, resilience, and environmental protection.





Leave a Reply