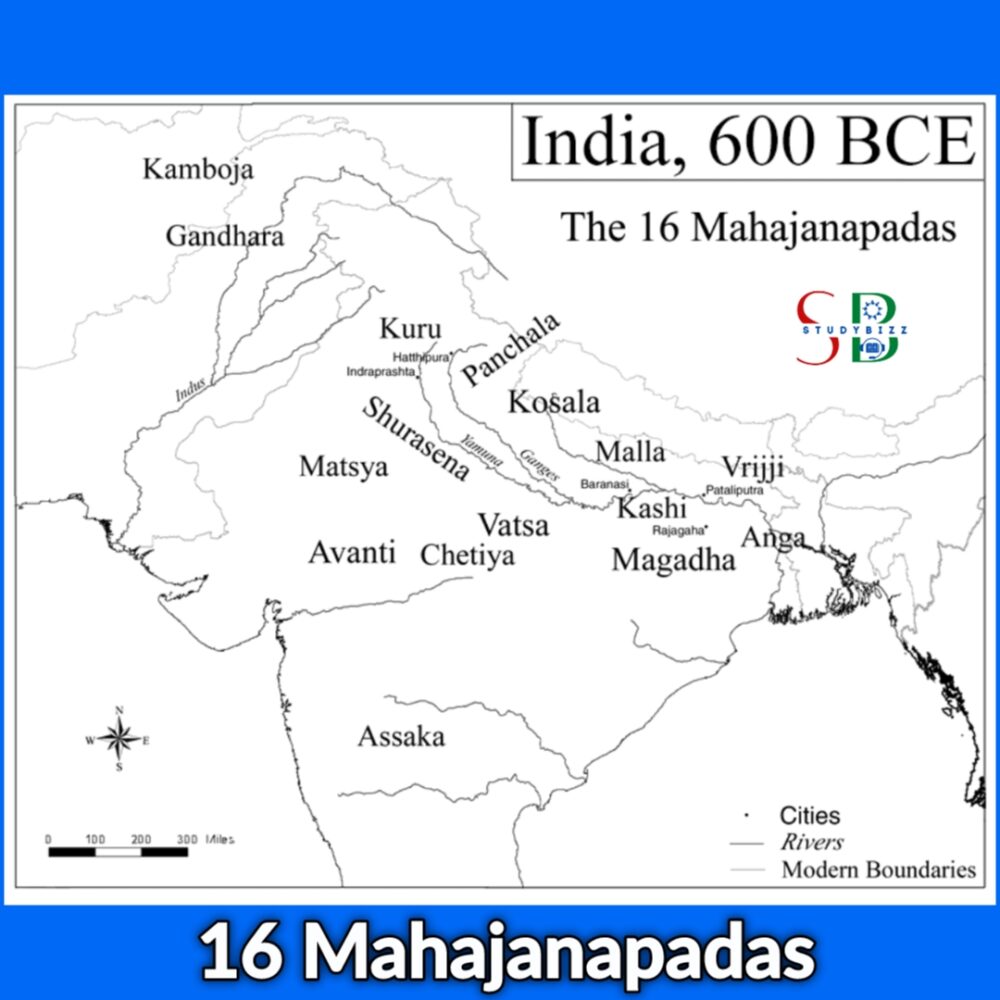
The Mahajanapadas were ancient Indian kingdoms or republics that existed between the 6th century BCE to 4th century BCE. There were 16 major Mahajanapadas and several smaller ones, which were located in the regions of present-day India, Pakistan, Nepal, and Bangladesh. The names of the 16 major Mahajanapadas are:
- Anga
- Magadha
- Kosala
- Vajji or Vriji
- Malla
- Chedi or Cheti
- Vatsa or Vamsa
- Kuru
- Panchala
- Matsya
- Kashi
- Assaka or Ashmaka
- Avanti
- Gandhara
- Kamboja
- Surasena
Most of these Mahajanapadas were ruled by kings and were often at war with one another. They were also loosely affiliated with each other through trade and political alliances. Some of the most prominent Mahajanapadas were the Kosala and Magadha kingdoms, which were located in present-day Uttar Pradesh and Bihar respectively. The Mahajanapadas were an important political and cultural development in ancient India, they were the precursor to the emergence of larger and more powerful empires, such as the Maurya and Gupta empires.
Anga : ( capital Champa )
- Anga was one of the 16 major Mahajanapadas, a political entity in ancient India during the time of the Buddha (6th century BCE to 4th century BCE)
- Anga was located in present-day eastern India, in the region that is now the state of Bihar and the northern parts of West Bengal.
- Anga was known for its powerful army and had a strong navy.
- Anga was ruled by a king and had a capital city called Champa
(also known as Campa or Champapuri).
- Anga was a major center of trade, particularly in textiles and agriculture.
- Anga was conquered by the Magadha kingdom, which went on to become one of the most powerful Mahajanapadas.
- The Anga kingdom was also ruled by king Pandu and his sons, who were the heroes of the Indian epic Mahabharata.
- Anga was one of the important kingdom where Buddhism spread and many Buddhist texts mentions this kingdom.
- The Pali texts of Buddhism also mention the Anga kingdom, and it is believed that the Buddha visited the kingdom and preached there.
Magadha : ( Capital : Rajagriha/Pataliputra )
The Magadha kingdom was one of the 16 Mahajanapadas, or major political entities, in ancient India. It was located in the modern-day Indian states of Bihar and Bengal. The capital of Magadha was Rajagriha, later known as Pataliputra. The kingdom was known for its powerful and centralized government, which was ruled by the Haryanka, Shishunaga, and Nanda dynasties. The Nanda dynasty was eventually succeeded by the Maurya Empire, which was founded by Chandragupta Maurya in the 4th century BCE. The Maurya Empire was one of the largest empires in the world at the time, and it was ruled by the famous emperor Ashoka.
Kosala : ( Capital : Shravasti )
The Kosala kingdom was one of the 16 Mahajanapadas, or major political entities, in ancient India. It was located in the northern region of the Indian subcontinent, in what is now the modern-day Indian state of Uttar Pradesh and the Nepalese Terai. The capital of Kosala was Ayodhya, and the kingdom was ruled by the Ikshwaku dynasty, who claimed descent from the sun god Surya.
- Kosala was one of the most powerful and prosperous of the Mahajanapadas.
- It was known for its strong and centralized government and powerful army.
- The kingdom was closely associated with the teachings of the Hindu sage Rishi Vasistha, who was the royal guru of the Ikshwaku kings.
- The most famous king of Kosala was King Dasaratha, the father of Lord Rama, the hero of the Hindu epic Ramayana.
- The kingdom was annexed by the powerful Magadha kingdom during the reign of the king Ajatashatru.
- Kosala was a powerful center of Vedic culture, and it is also mentioned in Buddhist texts as one of the key places visited by the Buddha during his lifetime.
Vajji or Vriji : ( Capital: Vaishali )
The Vajji kingdom was one of the 16 Mahajanapadas, or major political entities, in ancient India. It was located in the present-day Indian state of Bihar and Nepal’s Terai region. The capital of Vajji was Vaishali, and the kingdom was ruled by a confederacy of tribes known as the Vajjis or Vrijis.
- Vajji was known for its republican form of government, with a council of elected leaders known as the “Vajjian Sangha” governing the kingdom.
- It was one of the few republics in ancient India, and its system of government influenced the development of the later Mauryan Empire.
- Vajji was a powerful kingdom and it was able to successfully resist the expansionist attempts of the Magadha kingdom for a long time.
- It was also an important center of Buddhism, as the Buddha is said to have delivered many sermons in Vaishali, and it was also the site of the second Buddhist council.
- The kingdom was eventually conquered by the powerful Magadha king, Ajatashatru.
Malla : ( Capital : Pawa and Kusinara )
The Malla kingdom was one of the 16 Mahajanapadas, or major political entities, in ancient India. It was located in the present-day northern Indian state of Uttar Pradesh and the Terai region of Nepal. The capital of Malla was Kusinara, and the kingdom was ruled by a powerful and centralized government.
- The Malla kingdom was known for its strong army and it is said to have successfully repelled invasions from neighboring kingdoms.
- It was a center of art, culture and trade, and it had a developed system of law and administration.
- The Malla kingdom was divided into two branches: Pawa Malla and Kashi Malla.
- It was also an important center of Buddhism, as the Buddha is said to have delivered his last sermons in Kusinara, and it was the site of the fourth Buddhist council.
- The kingdom was eventually conquered by the powerful Magadha king, Ajatashatru, and later it was annexed by the kingdom of Kosala.
Chedi or Cheti : ( Capital : Suktimati )
The Chedi kingdom was one of the 16 Mahajanapadas, or major political entities, in ancient India. It was located in the present-day Indian state of Madhya Pradesh and Chhattisgarh. The capital of Chedi was Suktimati, and the kingdom was ruled by a powerful and centralized government.
- Chedi kingdom was known for its strong army and it’s said to have successfully repelled invasions from neighboring kingdoms.
- It was a center of trade and commerce, and it had a developed system of law and administration.
- The Chedi kingdom was ruled by a powerful dynasty of kings, who were known for their wealth and military prowess.
- It was also an important center of Buddhism, as the Buddha is said to have visited the kingdom during his lifetime and it was the site of the third Buddhist council.
- The kingdom was eventually conquered by the powerful Magadha king, Ajatashatru.
- The Chedi kings were also mentioned in the famous Indian epic ‘Mahabharata’ as allies of the Kuru dynasty.
Vatsa or Vamsa : ( Capital : Kaushambi )
- The Vatsa kingdom was one of the 16 Mahajanapadas, or major political entities, in ancient India. It was located in the present-day northern Indian state of Uttar Pradesh and the Terai region of Nepal.
- The capital of Vatsa was Kaushambi, and the kingdom was ruled by a powerful and centralized government.
- The kingdom was known for its strong army and it is said to have successfully repelled invasions from neighboring kingdoms.
- It was a center of art, culture and trade, and it had a developed system of law and administration.
- The Vatsa kingdom was also an important center of Buddhism and it was visited by the Buddha during his lifetime.
- It was also known for its association with the philosopher and grammarian Pāṇini, who was a native of the kingdom.
- The kingdom was also known for its contribution to the field of music and dance.
- The kingdom was eventually conquered by the powerful Magadha king, Ajatashatru.
Kuru : ( Capital : Indapatta)
- The Kuru kingdom was one of the 16 Mahajanapadas, or major political entities, in ancient India. It was located in the present-day Indian state of Haryana and parts of western Uttar Pradesh.
- The capital of Kuru was Indapatta (modern-day Indauli) and the kingdom was ruled by a powerful and centralized government.
- The Kuru kingdom was known for its strong army and it is said to have successfully repelled invasions from neighboring kingdoms.
- It was a center of art, culture and trade, and it had a developed system of law and administration.
- Kuru was also an important center of Vedic culture and many famous sages like Jaimini, Paila and Vaisampayana were associated with Kuru kingdom.
- The Kuru dynasty was also known for being the main clan involved in the Kurukshetra War, which is described in the epic Mahabharata.
- The kingdom was eventually conquered by the powerful Magadha king, Ajatashatru.
Panchala : ( Capital: Ahichatra )
- The Panchala kingdom was one of the 16 Mahajanapadas, or major political entities, in ancient India. It was located in the present-day northern Indian states of Uttar Pradesh and Uttarakhand.
- The capital of Panchala was Ahichatra, and the kingdom was ruled by a powerful and centralized government.
- It was known for its strong army and it is said to have successfully repelled invasions from neighboring kingdoms.
- Panchala was an important center of Vedic culture and it was known for its association with the sage Yajnavalkya.
- The Panchala was also known for its association with the philosopher and grammarian Pāṇini, who was a native of the kingdom.
- The kingdom was also known for its contribution to the field of music and dance.
- The kingdom was eventually conquered by the powerful Magadha king, Ajatashatru.
Matsya : ( Capital : Viratanagara )
- The Matsya kingdom was one of the 16 Mahajanapadas, or major political entities, in ancient India. It was located in the present-day northern Indian state of Rajasthan.
- The capital of Matsya was Viratanagara, and the kingdom was ruled by a powerful and centralized government.
- It was known for its strong army and it is said to have successfully repelled invasions from neighboring kingdoms.
- Matsya was an important center of trade and commerce.
- The kingdom of Matsya was also known for its contribution to the field of music and dance.
- The Matsya kingdom was also known for its association with the sage, Raikva, who was a native of the kingdom.
- The kingdom was eventually conquered by the powerful Magadha king, Ajatashatru.
Kasi or Kashi : ( Capital : Kasi )
Assaka or Ashmaka : ( Capital : Potali/Podhana/Paudanya )
- The Ashmaka kingdom was one of the 16 Mahajanapadas, or major political entities, in ancient India. It was located in the present-day western Indian state of Maharashtra.
- The capital of Ashmaka was Paudanya, and the kingdom was ruled by a powerful and centralized government.
- Ashmaka was known for its strong army and it is said to have successfully repelled invasions from neighboring kingdoms.
- It was a center of trade and commerce, and it had a developed system of law and administration.
- The Ashmaka kingdom was also known for its association with the sage, Gautama Maharishi, who was a native of the kingdom and it was also known for its association with the sage Agastya.
- The kingdom was eventually conquered by the powerful Satavahana dynasty.
- Ashmaka was also known for its contribution to the field of music and dance.
Avanti : ( Capital : Ujjain or Mahishamati)
- The Avanti kingdom was one of the 16 Mahajanapadas, or major political entities, in ancient India. It was located in the present-day Indian state of Madhya Pradesh and parts of Gujarat and Maharashtra.
- The capital of Avanti was Ujjain or Mahishamati, and the kingdom was ruled by a powerful and centralized government.
- Avanti was known for its strong army and it is said to have successfully repelled invasions from neighboring kingdoms.
- It was a center of trade and commerce, and it had a developed system of law and administration.
- The Avanti kingdom was also known for its association with the sage, Vashistha, who was a native of the kingdom and it was also known for its association with the sage, Jaimini.
- Avanti was also known for its contribution to the field of music and dance.
- The kingdom was eventually conquered by the powerful Magadha king, Ajatashatru and later it was annexed by the Satavahana dynasty.
Gandhara : ( Capital : Taxila )
- The Gandhara kingdom was one of the 16 Mahajanapadas, or major political entities, in ancient India. It was located in the present-day northern Pakistan and eastern Afghanistan.
- The capital of Gandhara was Taxila, and the kingdom was ruled by a powerful and centralized government.
- Gandhara was known for its strong army and it is said to have successfully repelled invasions from neighboring kingdoms.
- It was a center of trade and commerce, and it had a developed system of law and administration.
- The Gandhara kingdom was also known for its association with the sage, Asvaghosa, who was a native of the kingdom.
- Gandhara was also an important center of Buddhism, as the Buddha is said to have visited the kingdom during his lifetime.
- The Gandhara kingdom was heavily influenced by Greek and Persian culture and art, due to its proximity to the Hellenistic kingdoms.
- The kingdom was eventually conquered by the powerful Magadha king, Ashoka, and later it was annexed by the Mauryan Empire.
Kamboja : ( Capital : Rajapura )
- The Kamboja kingdom was one of the 16 Mahajanapadas, or major political entities, in ancient India. It was located in the present-day regions of Afghanistan, Pakistan and Northern India (Kashmir, Himachal Pradesh and parts of Punjab and Uttar Pradesh)
- The capital of Kamboja was Rajapura, and the kingdom was ruled by a powerful and centralized government.
- Kamboja was known for its strong army and it is said to have successfully repelled invasions from neighboring kingdoms.
- It was a center of trade and commerce, and it had a developed system of law and administration.
- The Kamboja kingdom was also known for its association with the sage, Vashistha, who was a native of the kingdom.
- Kamboja was also an important center of Buddhism, as the Buddha is said to have visited the kingdom during his lifetime.
- The Kamboja kingdom was heavily influenced by Greek and Persian culture and art, due to its proximity to the Hellenistic kingdoms.
- The kingdom was eventually conquered by the powerful Magadha king, Ashoka, and later it was annexed by the Mauryan Empire.
Surasena : ( Capital : Mathura )
- The Shurasena kingdom was one of the 16 Mahajanapadas, or major political entities, in ancient India. It was located in the present-day northern Indian state of Uttar Pradesh and the Terai region of Nepal.
- The capital of Surasena was Mathura, and the kingdom was ruled by a powerful and centralized government.
- Shurasena was known for its strong army and it is said to have successfully repelled invasions from neighboring kingdoms.
- It was a center of trade and commerce, and it had a developed system of law and administration.
- The Surasena kingdom was also known for its association with the sage, Uddhava, who was a native of the kingdom and it was also associated with the life of the historical figure, Lord Krishna, who was born in Mathura and said to have ruled the Shurasena kingdom as well as Surasena kingdom.
- The Surasena Mahajanapada played an important role in the political and cultural history of ancient India. It was an important center of trade and commerce and was strategically located on the trade routes between the Gangetic plain and western India. It was also a center of learning and attracted many scholars and philosophers.
- The kingdom was eventually annexed by the Mauryan Empire in the 4th century BCE, and its people became an integral part of the Mauryan polity. However, the legacy of the Surasena Mahajanapada continued to influence the cultural and religious traditions of the region for centuries to come.




Leave a Reply