Godavari River :
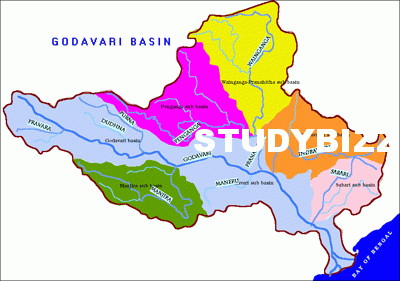
The Godavari is the India’s second longest river after the Ganga and third largest in India and Largest river in South India.
It drains about 10% of India’s total geographical area.
Source of Origination:Trimbakeshwar, Nashik, Maharashtra.
Total Length : 1,465 kilometres (910 mi) from west to east.
Draining States: Maharashtra (48.6%), Telangana (18.8%), Andhra Pradesh (4.5%), Chhattisgarh (10.9%) and Odisha (5.7%). [Including tributaries]
The river ultimately empties into the Bay of Bengal through an extensive network of tributaries.
River Basin Area: 312,812 km2 (120,777 sq mi)
It forms one of the largest river basins in the Indian subcontinent, with only the Ganga and Indus rivers having a larger drainage basin.
In terms of length, catchment area and discharge, the Godavari is the largest in peninsular India, and had been termed as the ganges of the south or dakshina ganga
| Salient Features of Godavari Basin | ||
|---|---|---|
| Basin Extent Longitude Latitude | 73° 24′ to 83° 4′ E 16° 19’ to 22° 34’ N | |
| Total drainage area of the Basin | 3,12,812 Sq.km | |
| State | Area in Sq.km | Percentage (%) |
| Maharashtra Telangana Andhra Pradesh Chhattisgarh Madhya Pradesh Odisha Karnataka Puducherry | 152,199 62,150 11,048 33,434 31,821 17,752 4,405 3 | 48.66 19.87 3.53 10.69 10.17 5.67 1.41 0.001 |
| Total Length of the River | 1465 km | |
| Length in Telangana & AP | 772 km | |
| * Average Yield | 113.09 BCM | |
| * 75% dependable Yield | 88.39 BCM | |
| * Major part of rainfall | Southwest monsoon period (July-Sept.) | |
| * Average Annual rainfall | 1110 mm | |
| Climate | Tropical |
Tributaries of Godavari River :
Upper Godavari (G-1)
Upper Godavari includes the reach of the river Godavari from its source to its confluence with Manjira and its drainage area lies entirely in Maharashtra. It excludes the catchment area of Pravara, Purna and Manjira and includes that of all other tributaries which fall into the Godavari in this reach. Main water resources projects in this sub-basin are Gangapur dam, Darna dam on Darna river; Nandur – Madhameshwar Pickup weir, Jaikwadi dam and Majalgaon dam on Sindhphana river.
Pravara (G-2)
The Pravara originates in the Western Ghats, flows in an easterly direction and falls into the Godavari upstream of Jaikwadi dam. Mula is one of its important tributaries. Its drainage area falls entirely in Maharashtra. Main water resources projects are Bhandardara dam, Nilvande dam and Mula dam.
Purna (G-3)
The Purna originates in the Ajanta Range of hills, flows in a south-easterly direction and joins the Godavari near Purna town. Its drainage area lies entirely in Maharashtra. The Purna receives several large tributaries, the chief on the north bank being Damna and Kailna and on the south bank Arjna, Girja and Dudhana. Main water resources projects are Khadakpurna dam, Yeldari dam, Siddheshwar dam and Dudhana dam.
Manjira (G-4)
Manjira is the longest tributary of Godavari. It is an inter-State river flowing through Maharashtra, Karnataka and Telangana. It originates in Balaghat range of hills, runs in south-east direction up to Manjira barrage in Telangana and from there in north direction till its confluence with Godavari. The principal tributaries of Manjira are Terna, Karanja and Haldi joining it from right side; and Lendi and Maner which join from the left. Manar, Lendi and Terna dams in Maharashtra; Karanja dam in Karnataka and Singur and Nizam Sagar dams in Telangana are the main water resource projects in Manjira sub-basin..
Middle Godavari (G-5)
It comprises the river Godavari from its confluence with the Manjira to its confluence with Pranahita. It is an inter- State sub-basin between the States of Telangana and Maharashtra. It includes the direct catchment of the Godavari in this reach as well as that of its tributaries, except Maner and Pranahita. Main water resources projects are Pochampad dam, Kadam dam, Sripad Yellampalli barrage, Sundilla barrage and Annaram barrage. The last two barrages are part of Kaleshwaram project
Maner (G-6)
The river Maner (the right bank tributary) originates at an altitude of about 533 m in Rajanna Sirisilla district of Telangana and it joins the Godavari river at an altitude of about 105 m upstream of Annaram barrage. The entire catchment of the Maner lies in the State of Telangana. Upper Maner, Middle Maner and Lower Maner dams are the main water resource projects in this sub-basin.
Penganga (G-7)
Penganga includes the entire catchment of the Penganga from its source to its confluence with the Wardha with all its tributaries. It is an inter-State sub-basin between the States of Telangana and Maharashtra and forms inter-State boundary between the two States. Kayadhu, Pus, Arunavati, Waghadi and Khuni are important tributaries. Main water resources projects are Upper Penganga dam, Upper Pus, Lower Pus, Arunavati dam, Waghadi dam and Saikheda dam.
Wardha (G-8)
Wardha comprises river Wardha from its source to its confluence with the Wainganga with all its tributaries but excluding the catchment of the Penganga. It is an inter-State sub-basin among the States of Madhya Pradesh, Maharashtra and Telangana. It also forms boundary between the States of Maharashtra and Telangana before its confluence with Wainganga. Bembla and Wunna are important tributaries. Main water resources projects are Bembla dam, Upper Wardha dam and Lower Wardha dam.
Pranahita (G-9)
Pranahita is the largest tributary of the Godavari covering about 34% of its drainage basin. It is an inter-State sub-basin among the States of Madhya Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, Maharashtra and Telangana. Main Pranahita river forms boundary between the two States of Telangana and Maharashtra. It carries the combined waters of the Penganga, the Wardha and the Wainganga after confluence of Wardha and Wainganga. It meets Godavari River from its left bank about 304 km below the Manjira confluence near Kaleshwaram temple town. Important tributaries are Bagh, Wainganga, Bawanthadi, Pench, Kanhan, Chulband, Garvi, Andhari, Kobragarhi, Dina nadhi and Peddavagu. Some of the water resources projects are Upper Wainganga, Dhuti weir, Thanwar dam, Bawanthadi dam, Bagh dam, Totaladoh dam, Itiadoh dam, Lower Chulband dam and Gosikhurd dam.
Lower Godavari (G-10)
Lower Godavari consists of the Lower part of the river Godavari from its confluence with the Pranahita upto the sea. The sub basin includes the direct catchment of the Godavari in this reach with all its tributaries except Indravati and Sabari. It is an inter-State sub-basin among the States of Telangana, Maharashtra, Chhattisgarh and Andhra Pradesh. In this sub-basin, Godavari forms boundary between the States of Maharashtra and Telangana; between the States of Telangana and Chhattisgarh. Some of the tributaries are Taliperu, Lakhnawarm, Peddvagu, Kinnerasani. Some of the existing and under construction water resources projects are Medigadda barrage and Pump house, Godavari LIS, Tupakulagudem barrage, Sitaram LIS, Dummugudem barrage, Polavaram dam, Pattisema LIS, Pushkar LIS, Purushottapatnam LIS, Chintalpudi LIS, Chagalnadu LIS, Venkatanagaram LIS and Aurthur Cotton barrage on main Godavari; and Laknawaram dam, Taliperu dam, Peddavagu dam, Kinnerasani dam on tributaries.
Indravati (G-11)
Indravati is the 2nd largest tributary of Godavari. It originates on the western slopes of the Eastern Ghats at an altitude of 915 m in Kalahandi district, Odisha State flows through the central part of the Dandakaranya region and joins Godavari approximately 40 km downstream of its confluence with Pranhita. It has its catchment in Odisha, Chhattisgarh and Maharashtra. Its important tributaries are Narangi, Boardhig, Kotri, Nibra and Bandia on the right and Nandiraj and Dantewara on the left. Important water resources project is Upper Indravati dam in Odisha..
Sabari (G-12)
Sabari is the last tributary of the Godavari. It originates at an altitude of 1,220 m in the Sinkaram hill range of the Eastern Ghats in Koraput district of Odisha. After flowing for an initial short distance in north, north-westerly and westerly direction, it turns south and flows in south-westerly direction up to its confluence with the Godavari river in the State of AP near Rudramkota town. Potteru is another important tributary of Sabari joining on the left side. Machkund or Sileru is the major tributary of Sabari on the left bank. Sabari receives some water of Indravati also through natural link of Joura Nalla. The important water resources projects are Upper Kolab dam, Jalaput dam, Machkund PH, Balimela dam, Balimela PH, Potteru weir, Guntwada weir, Upper Sileru PH, Donkarayi dam and Lower Sileru Power house..